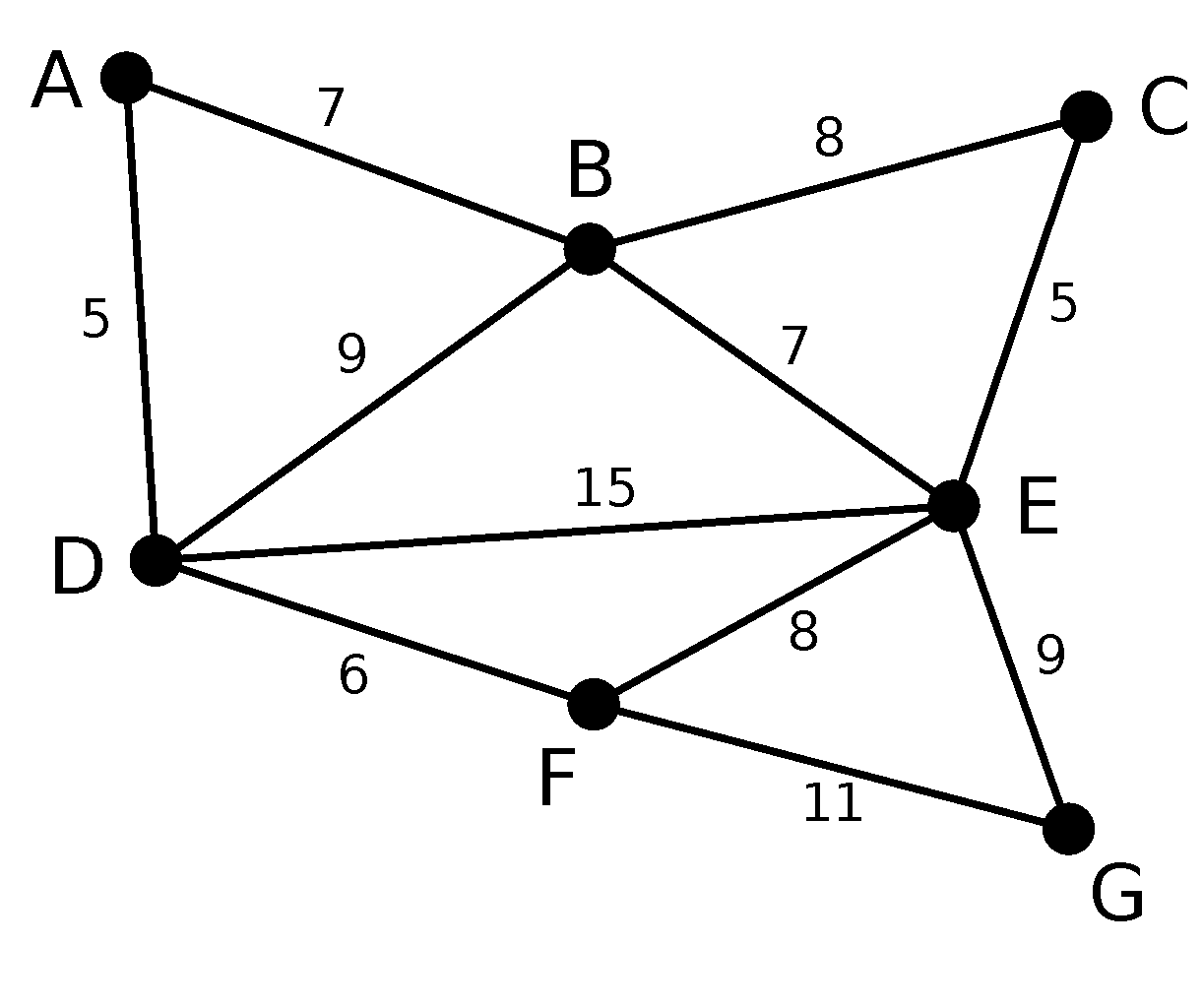
Minimum Spanning Tree
最小生成树主要分为两种算法:Kruskal 还有 Prim。
参考:
Kruskal
Kruskal 的优势在于好写
动画(来自USACO guide)
这也有张图(来自oi-wiki):
思路
算法思路很简单,基于贪心思想:初始联通集合为空,给所有的边的权值从小到大排序(可以使用一些像 set的数据结构),每次拿最小的边,连接到合集中,看和现有联通的点行不形成环,或者说联通的点有没有多(可以用 dsu来查询)。如果没有就放弃这条边,有的话就加入集合。
复杂度
假设图有E条边,V个定点;
- 时间复杂度:排序的时间复杂度是:O(E\log E),并查集操作: O(E \times \alpha(v))\approx O(E),所以总时间复杂度是O(E\log E)
- 空间复杂度:O(E+V)
实现
来自 GPT4o老师:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
class DSU {
private:
vector<T> parent; // Stores the parent of each element
vector<T> rank; // Stores the rank (used for union by rank)
public:
// Constructor to initialize the DSU
DSU(T n) {
parent.resize(n);
rank.resize(n, 1); // Initialize ranks to 1
for (T i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
parent[i] = i; // Initially, each element is its own parent
}
}
// Find operation (with path compression)
T find(T x) {
if (parent[x] != x) {
parent[x] = find(parent[x]); // Path compression to flatten the tree
}
return parent[x];
}
// Union operation (union by rank)
bool unite(T x, T y) {
T rootX = find(x);
T rootY = find(y);
if (rootX == rootY) {
return false; // If both elements are in the same set, no need to union
}
// Union by rank: attach the smaller tree under the larger tree
if (rank[rootX] < rank[rootY]) {
parent[rootX] = rootY;
} else if (rank[rootX] > rank[rootY]) {
parent[rootY] = rootX;
} else {
parent[rootY] = rootX;
rank[rootX] += 1; // Increase the rank if the roots are of equal rank
}
return true; // Union was successful
}
};
// Structure to represent an edge in the graph
template <typename T>
struct Edge {
T u; // Start vertex of the edge
T v; // End vertex of the edge
T weight; // Weight of the edge
// Comparator for sorting edges by weight
bool operator<(const Edge& other) const {
return weight < other.weight;
}
};
// Kruskal's Algorithm to find the Minimum Spanning Tree (MST)
template <typename T>
T kruskal(T V, vector<Edge<T>>& edges, vector<Edge<T>>& mst) {
// Step 1: Sort all edges by weight
sort(edges.begin(), edges.end());
// Step 2: Initialize DSU for connected components
DSU<T> dsu(V);
// Step 3: Iterate through sorted edges and construct the MST
T totalWeight = 0; // Total weight of the MST
for (const Edge<T>& edge : edges) {
if (dsu.unite(edge.u, edge.v)) { // If the edge does not form a cycle
mst.push_back(edge); // Add the edge to the MST
totalWeight += edge.weight; // Add the edge weight to the total
}
}
return totalWeight; // Return the total weight of the MST
}
int main() {
// Example usage
int V = 5; // Number of vertices
vector<Edge<int>> edges = {
{0, 1, 10},
{0, 2, 6},
{0, 3, 5},
{1, 3, 15},
{2, 3, 4}
};
vector<Edge<int>> mst; // To store the edges of the MST
// Run Kruskal's algorithm
int mstWeight = kruskal<int>(V, edges, mst);
// Output the MST
cout << "Edges in the Minimum Spanning Tree:\n";
for (const auto& edge : mst) {
cout << edge.u << " -- " << edge.v << " == " << edge.weight << "\n";
}
cout << "Total weight of the MST: " << mstWeight << "\n";
return 0;
}
Prim
Prim算法的优势在于适合稠密图。
思路
Prim算法基于贪心思想,但与Kruskal不同的是:
- Kruskal是按边贪心
- Prim是按点贪心
具体来说,Prim算法从任意一个起点开始,维护一个已访问点的集合。每次从所有连接"已访问点集合"和"未访问点集合"的边中选取权值最小的边,并把对应的点加入已访问集合。重复这个过程直到所有点都被访问。
复杂度
假设图有E条边,V个顶点:
- 时间复杂度:使用二叉堆优化的版本是O(E\log E);使用斐波那契堆可以优化到O(E+V\logV);不使用堆的朴素版本是O(V^2)
- 空间复杂度:O(E+V)
实现
来自 Claude 3.5老师:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <limits>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
struct Edge {
T to; // Target vertex
T weight; // Edge weight
// Comparator for priority queue
bool operator>(const Edge& other) const {
return weight > other.weight;
}
};
// Implementation of Prim's algorithm
template <typename T>
T prim(vector<vector<Edge<T>>>& graph, vector<Edge<T>>& mst) {
int V = graph.size(); // Number of vertices
// Track visited vertices
vector<bool> visited(V, false);
// Priority queue (min-heap) to store edges
priority_queue<Edge<T>, vector<Edge<T>>, greater<Edge<T>>> pq;
T totalWeight = 0; // Total weight of MST
// Start from vertex 0
visited[0] = true;
// Add all adjacent edges of starting vertex to priority queue
for (const Edge<T>& e : graph[0]) {
pq.push(e);
}
// Continue while priority queue is not empty
while (!pq.empty() && mst.size() < V - 1) {
Edge<T> curr = pq.top();
pq.pop();
// Skip if target vertex is already visited
if (visited[curr.to]) {
continue;
}
// Add edge to MST
mst.push_back(curr);
totalWeight += curr.weight;
// Mark target vertex as visited
visited[curr.to] = true;
// Add all unvisited adjacent edges of new vertex to priority queue
for (const Edge<T>& e : graph[curr.to]) {
if (!visited[e.to]) {
pq.push(e);
}
}
}
return totalWeight;
}
int main() {
// Example usage
int V = 5; // Number of vertices
vector<vector<Edge<int>>> graph(V);
// Add edges (undirected graph)
auto addEdge = [&](int u, int v, int w) {
graph[u].push_back({v, w});
graph[v].push_back({u, w});
};
addEdge(0, 1, 10);
addEdge(0, 2, 6);
addEdge(0, 3, 5);
addEdge(1, 3, 15);
addEdge(2, 3, 4);
vector<Edge<int>> mst; // Store MST edges
// Run Prim's algorithm
int mstWeight = prim(graph, mst);
// Output MST
cout << "Edges in Minimum Spanning Tree:\n";
for (const auto& edge : mst) {
cout << " -- " << edge.to << " == " << edge.weight << "\n";
}
cout << "Total weight of MST: " << mstWeight << "\n";
return 0;
}